The internet can be a dangerous place, but taking collective action, investing in education and adopting new tech can help tame it.
Communication technologies, platforms, and companies are critical for global commerce and most people’s social lives. These businesses can also be some of the most vulnerable forms of technology. Here are seven encouraging trends making a positive difference regarding threats in communications.
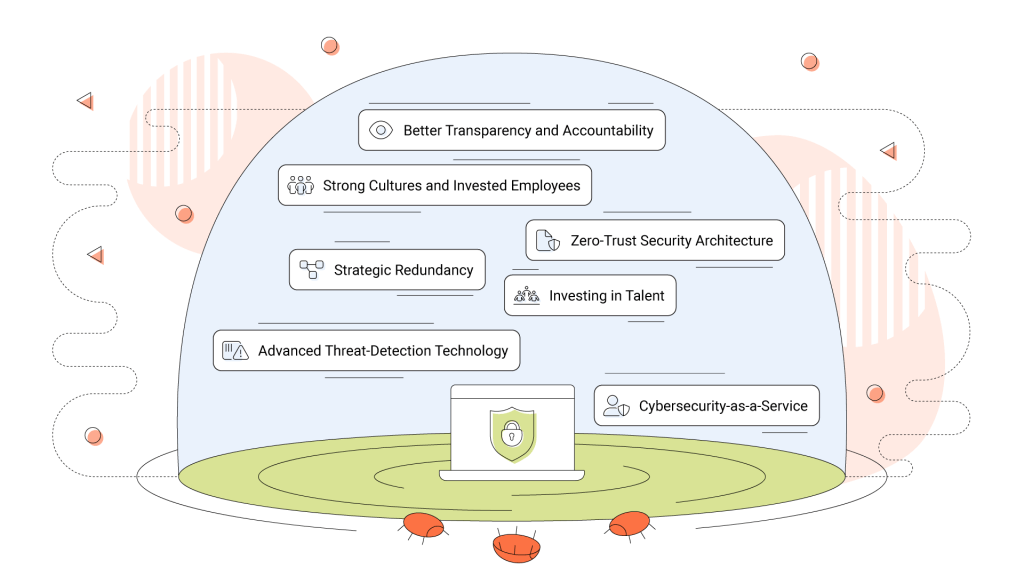
- Better Transparency and Accountability
- Strong Cultured and Invested Employees
- Zero-Trust Security Infostructure
- Strategic Redundancy
- Investing in Talent
- Cybersecurity-as-a-Service
- Advanced Threat-Detection Technology
1. Better Transparency and Accountability
The Center for Strategic and International Studies maintains a list of significant cyber incidents. The attacks from 2022 include the following, among many others, against telecommunication platforms and communication tools:
- Takeovers of the social media accounts of high-profile military organizations
- Takedowns of websites associated with governments and private companies
- Accusations of governments stealing telephone and internet data from other nations’ citizens
- Distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks render some communication channels unusable
- Successful attacks against public-address (PA) systems
- Phishing attacks gleaning credentials for Microsoft 365 and other productivity accounts
- Successful attacks against video-hosting websites
Of particular concern was the number of attacks where bad actors used communications channels like WhatsApp and social media to appear genuine and curry trust with their targets before leaning on them for classified information or credentials.
What is encouraging is the level of detail available today and the swiftness of disclosure. The technology and business communities have successfully raised the profile of cybersecurity incidents and worked toward a shared vocabulary and set of expectations for disclosure, remediation and restitution for security breaches. 2021 saw millions of dollars in fines levied against communications providers large and small, as well as various other company types.
2. Strong Cultures and Invested Employees
Strong culture and invested employees are two undervalued trends positively impacting cybersecurity threats in this sector. The easiest way to get these things in a business setting is to invest in training and people’s well-being.
Even moderately effective cybersecurity training programs for employees provide a strong return on investment. Additional research shows that most of the costs associated with cybersecurity breaches can be traced to successful phishing attacks against employees. And don’t just stop at traditional cybersecurity methods. By learning new skills like Solidity, a coding language used to write smart contracts, your business can stay secure on the blockchain.
Making employees aware is step one. Getting them invested is step two, which involves offering competitive compensation packages and providing a sense of or stake in the ownership of the organization.
3. Zero-Trust Security Architecture
Zero-trust security is another trend positively impacting threat landscapes in communications. According to a 2021 U.S. National Security memorandum, the core tenet of zero-trust architecture is to eliminate “trust in any one element, node or service.” Zero-trust has become the backbone of the U.S. government’s cybersecurity defense strategy.
Here’s how this applies to cybersecurity threats in communications:
- Zero-trust assumes every node is a security threat. Likewise, it surmises every communication will leak. This informs the content of internal communications and impacts security hygiene practices, like not emailing passwords.
- True zero-trust security architecture applies industry-standard end-to-end encryption to all data transmissions and communications.
- Zero-trust security eliminates text-based passwords as much as possible in favour of biometrics and unique cryptographic keys.
Even companies that transmit classified or controlled information have options. Standards like NIST 800-171 and DFARS 252.204-7012 outline how zero-trust security applies to any company that sends and receives highly protected information.
4. Strategic Redundancy
Having contingencies and expectations in place during cyber emergencies is one of the marks of preparedness for the modern company. Some cybersecurity experts say it’s less a case of “if” and more a matter of “when” any given company gets hacked.
When a company does experience a cyberattack, it’s fair to assume its preferred digital communications platforms and infrastructure would also become compromised or unavailable. For this reason, businesses are diversifying and creating redundancies in the apps and services they use to stay connected.
This may involve phone trees and other offline communication flows to spread the word during cyberattacks or other disruptive events quickly. Other companies invest in secondary communication platforms or apps they can automatically transition workflows to during disruptions to avoid losing data or productivity.
Technology enables communication redundancy at the local level with municipalities and first responders. Natural disasters are a significant and constant threat to communication infrastructure. However, miniaturizing and mobilizing the technologies in cell towers and another infrastructure gives residents, businesses, and emergency responders the tools they need to stay in touch even during the harshest conditions.
5. Investing in Talent
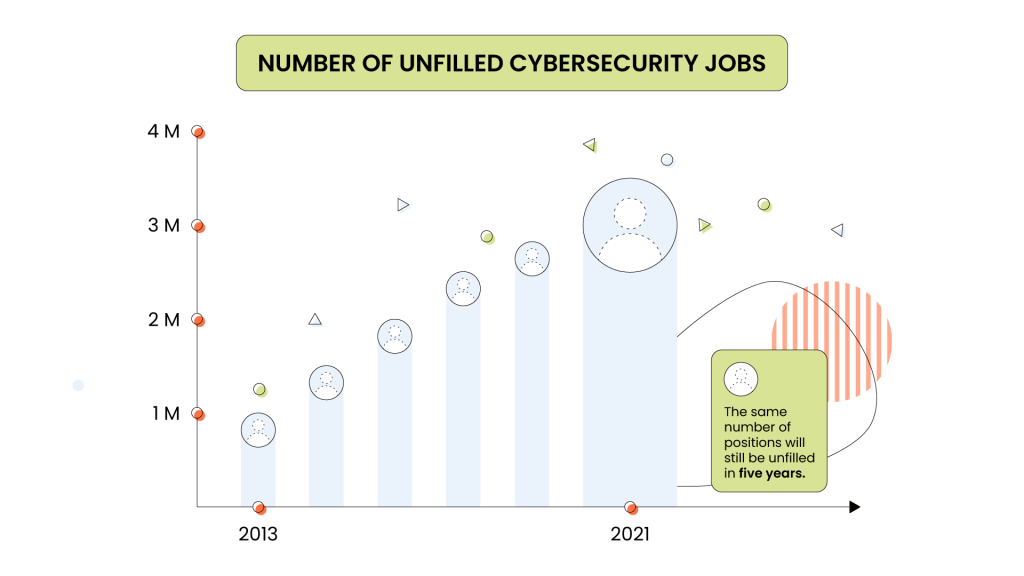
The demand for skilled cybersecurity workers is growing far faster than schools can turn out qualified graduates. The number of unfilled cybersecurity jobs grew from 1 to 3.5 million worldwide between 2013 and 2021. This research also says the same number of positions will still be unfilled in five years.
The bad news is that companies can’t always hire the in-house talent they need to invest in cybersecurity preparedness. However, these numbers reveal that people are aware of the problem. The number of companies seeking to invest in this kind of talent shows that cybersecurity awareness is on the rise among businesses of all sizes.
6. Cybersecurity-as-a-Service
Companies that can’t hire cybersecurity talent directly for whatever reason, including budget limitations, often do well with cybersecurity-as-a-service (CaaS). This industry is poised to grow by more than 10% annually between 2021 and 2028.
In most cases, CaaS is a monthly fee, and companies receive cutting-edge third-party cybersecurity products and experience. CaaS frees communications companies from building their own security measures into their apps, platforms and services. It allows them to innovate on their core products instead of focusing on security elements.
7. Advanced Threat-Detection Technology
The services and channels providing communications connectivity worldwide face countless daily threats that seek to take them offline or extort them. The most advanced cybersecurity technology available offers advanced threat detection and automation capabilities. The increasing adoption of IoT in telecom has brought new cybersecurity challenges that require innovative solutions to protect against potential threats. According to IBM, applying automated security tools could shield organizations from around 80% of cyber threats.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is the power behind a lot of this automation. One of the ways AI can do some societal good is by automating some of the cybersecurity work that takes up so much of the average specialist’s time. This means automatically scanning for, flagging and isolating suspicious traffic on company networks or communication channels.
AI is keeping online communication platforms safe from various threats as well. One way is through automatic flagging of potentially dangerous, inflammatory or factually incorrect language. There will always be a case for human subject-matter experts to make the final call. However, AI can do a lot of the heavy lifting when it comes to moderating digital communications and making them safer for all participants.
Protecting the Communications Field
Communications is an enormous field encompassing:
- The companies providing communication technologies and channels, like telecom businesses, internet service providers and video-hosting websites
- Organizations whose product is a form of communication – like PR companies, nonprofits and publishers
- The technologies facilitating information and data exchanges between stakeholders, like IT infrastructure, email and chat apps, blockchain, and machine-to-machine communication (IoT)
All these aspects of modern communication deserve consideration when it comes to cyber threats. Happily, many of the encouraging trends and consequential technologies within cybersecurity are universal, no matter the discipline.