Telemedicine is a new direction in the healthcare industry that’s been developing for several years. Just to give you some numbers, before the pandemic swept the world in 2020, the telemedicine market was worth $49.9 and is expected to grow to 20% by 2026.
Today, those numbers have skyrocketed and are projected to reach $439 billion by 2030. This can mean only one thing: interest in the mobile app market hasn’t gone anywhere and remains as strong as ever.
In the article, we will tell you all about what telemedicine is, why it’s important, and what benefits telemedicine apps provide to doctors and patients. We’ll also explain how to build such an app from scratch, so you can start your telemedicine business with no fuss.
- What is a Telemedicine App?
- The Benefits of Telemedicine Applications
- Technologies Behind Telemedicine Application
- The Essential Features of a Telemedicine Platform
- How to Develop a Telemedicine Application
- How Much Does it Cost to Build a Telemedicine App

What Is a Telemedicine App?
The term “telemedicine” is used to describe the process of providing healthcare to patients through remote appointments using electronic information and technology. Most often, these appointments are delivered via video calls, although instant messaging mode and emails are quite common, too.
A telemedicine app, as can be guessed from the above, is the means to use telemedicine services. It’s worth pointing out that telemedicine apps are not the same, though. Depending on the nature of services, they can be of three types, including:
- Remote patient monitoring
- Store-and-forward medicine
- Real-time interactive medicine
Let’s briefly touch upon each of them to understand the difference.
Remote Patient Monitoring
Apps in this category are tailored for people who need health monitoring for certain health conditions, such as heart disease, high blood pressure, or post-surgery check-ups. Rather than driving to the clinic and sitting in a waiting room, patients can be administered from a distance in the comforts of their own homes through telemonitoring.
Real-Time Interactive Medicine
The distinct feature of real-time telemedicine apps is that they can be integrated with chat API service and allow people to get immediate doctor advice through any of the available mediums, including but not limited to video conferences, phone calls, instant messages, or home visits when necessary.
Store-And-Forward Medicine
Unlike the two others, store-and-forward medicine apps work in a similar way to emails, where people can share their medical information through a telemedical platform. The advantage of these apps is that they make it possible to connect with specialists from any healthcare discipline while ensuring the security of a patient’s data.
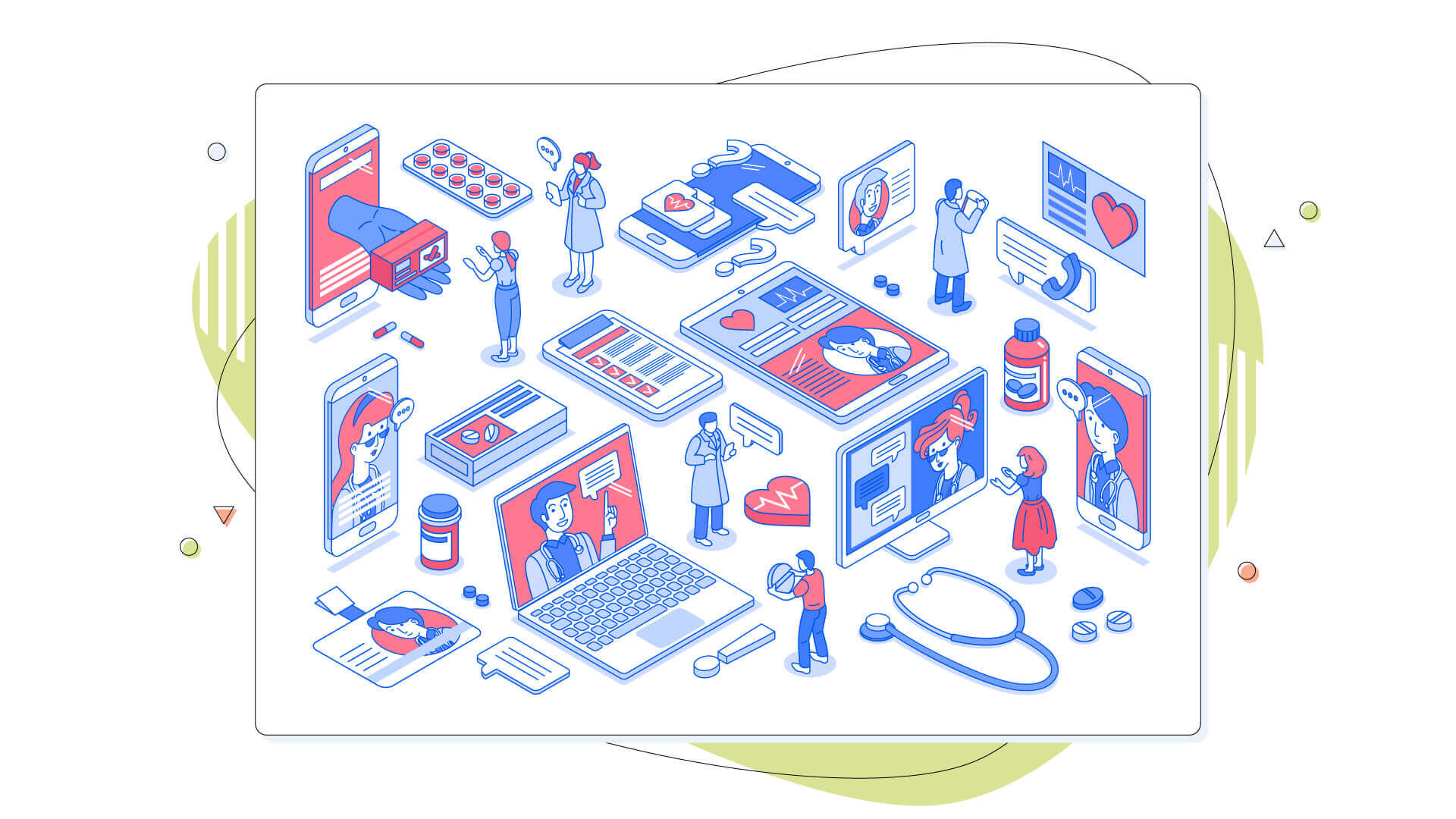
The Benefits of Telemedicine Applications
Without a doubt, the most important benefit of a telemedicine app is that it helps lessen the overload on hospitals by making healthcare more accessible to people. However, this is not the only benefit it offers. To better understand the telemedicine benefits, let’s divide them into two groups and view each one separately:
- Benefits for patients;
- Benefits for doctors.
The Benefits for Patients
Of course, one of the biggest advantages of a telemedicine platform is convenience. With its help, people don’t need to drive to the doctor’s office every time they worry about something and can receive a medical consultation immediately. For young families with kids, this can be a real lifesaver.
The second advantage follows from the first. Because telemedicine apps allow people to access appointments with doctors from different locations, it helps them save a lot of waiting time. Unfortunately, shortages of doctors have become commonplace in many parts of the world, resulting in endless waiting lists for patients. However, telemedicine solves this issue.
Aside from that, visits scheduled via a telemedicine platform cost considerably less than doctor’s appointments. According to research, savings from “tele” visits vs. physical visits average $70, which is enough of a reason for many people to turn to telemedicine apps.
Last but not least, telemedicine opens doors to specialists from any geographical location, allowing you to skip a long waiting list and get to the right physician from anywhere in the world.
The Benefits for Doctors
Time is the most valuable resource, especially for doctors that have hundreds of patients on a waiting list. This is where telemedicine apps come in handy, giving them the ability to control their schedule and spend their time more efficiently.
Another advantage of telemedicine is that it helps improve clinical workflow. By analyzing each case based on the information provided to physicians through the platform, they can decide whether a patient visit is necessary or an online consultation will suffice.
In addition, telemedicine apps allow physicians to see more patients from all over the world. This can not only help them expand their practice but also increase user engagement and effectively reduce patient no-show appointments.
Of course, improved time management and fewer non-emergency cases to be dealt with effectively result in lower overhead costs for hospitals. Thanks to this, they can focus on some other healthcare sectors that need attention and improvement.

Technologies Behind Telemedicine Application
Now, with these benefits at hand, let’s dive into the technologies that are best suited for tele-app development. Here are the most popular of them:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Big data
- IoT (or IoMT)
- Blockchain
Artificial Intelligence
One of the most frequently used technologies for developing a telemedicine app, without a doubt, is Artificial Intelligence. In fact, it is thanks to AI that the use of chatbots, machine learning, voice recognition, and data collection has been made possible, all of which are the key components of any tele-app.
Big Data
Big data (BD) comes next on the list. Healthcare generates a lot of information, starting from contact details, demographics, locations to media files, and all this data should be utilized to make sense of it. With big data, this can be easily done. By leveraging the power of BD, e-health professionals can extract actionable insights from gigabytes of data and make better decisions as a result.
IoT (IoMT)
The Internet of Things (IoT) or The Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), modified for application in the healthcare market, is the next technology widely used in telemedicine. Essentially, this term encompasses all portable medical equipment designed to monitor vital health parameters like:
- Glucose levels
- Weight
- Pulse
- EKG
- Body temperature, etc.,
and send this data wirelessly to the cloud storage for further analysis by healthcare professionals.
Blockchain
Security is paramount for digital products and even more so for healthcare. That’s where blockchain comes into play. Known as one of the most secure ways to move and store data, blockchain gives users confidence that the data they share will not be stolen or accessed by unauthorized users in any way. Blockchain consulting firms can also provide valuable insights into how healthcare organizations can leverage the immutable nature of blockchain to enhance data integrity, streamline processes, and improve patient outcomes.
The Essential Features of a Telemedicine Platform
While telemedicine apps aren’t the same, there are a number of features that can be found in all of them. Depending on their complexity, they can be broken down into two groups:
- Basic;
- Advanced.
Basic Features
Basic features are called basic because they exist in all wellness applications. Here are the key components they include:
- User (Patient) Profile. This is a directory of user settings, including a patient’s full information, like their name, address, medical data, age, place of birth, and so on;
- Doctor Profile. As the name suggests, it is a profile directory of doctors containing information about their field of practice, contact details, and timetable;
- Location Tracking. With this tracker, users can search for nearby nurse practitioners and pharmacies using Google Maps.
- Electronic Health Records (EHR). The implementation of EHR allows medical practitioners to keep track of the latest updates on their patients’ records remotely;
- Communication Means. This can be any type of communication tool for two-party interaction, including instant messaging, audio calls, chats, video conferences, etc.
- Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM). Healthcare providers use RPM to monitor patient health from a distance without the need for them to carry manipulations on their own;
- Real-time Consultation. Also known as a symptom checker, this system allows users to get connected to the right doctor based on the symptoms they experience;
- Prescription Management. A lot of tele-apps send their patients push notifications to remind them to take meds.
Advanced Features
In addition to basic features, there must be some advanced features to distinguish one app from the other. These features may include:
- Cross Compatibility. Not all people are comfortable using smartphones, so it’s important to build an app that can be easily accessed across various devices;
- File Sharing. By enabling file sharing capability, doctors can make more accurate diagnoses without a patient’s visit;
- Moderation. To prevent the spread of spam messages and irrelevant images or calls, moderation tools can be used.

How to Develop a Telemedicine Application: 7 Steps
Now that we’ve covered the main technologies and features used for a telemedicine software development as well as the importance of developing one in the first place, we can finally get down to the process. For your convenience, we’ve broken it down into seven easy-to-follow steps.
1. Conduct Business Analysis
This is the first and most important step of app development that can help validate the viability of your idea and decide whether to proceed with it or not. At this point, you should be able to answer questions such as why you’re building a telehealth app, what problems it can solve for patients and doctors, and if there’s a demand for your app on the whole.
2. Research and Analyze Your Competitors
Take the time to research competitors. This will give you insights into their strengths and weaknesses, as well as give you an idea of the features that can be implemented in your app. Read user reviews and take note of the prices. With this info at hand, it will be easier to create a compelling app.
3. Plan an App Infrastructure
The next step after researching the market and analyzing the competition is to plan the infrastructure of your app, i.e., its functionality and communication tools. To do this, you must once again answer the question of how the app will help patients and doctors and how much budget you’re willing to invest in development.
4. Design an Appealing User Interface
Understanding who your users are, how old they are, where they live, and how they will use the app will help you put together a UX/UI design that will appeal to them. However, don’t overdo it with details. In this step, it’s important to focus on bookings and payments more than on anything else.
5. Select App Monetization Model
There’s no use in developing a tele-app if it can’t be monetized, so make sure to choose the most convenient monetization model for you and your users. In general, there are four most common types of monetization models to choose from:
- Freemium
- Paid
- Subscription
- In-app ads
Going from the name, freemium provides users with free access to the basic functionality of the app. To be able to use advanced features, they will need to upgrade and pay a certain fee.
Paid monetization model means what it says. A user will need to make a payment in order to download the app from the store.
Unlike the paid model, where users are expected to pay a one-time fee, a subscription implies paying a certain amount of money on a monthly/yearly basis.
There’s no charge for users when using the in-app advertising model. Instead, the revenue comes from in-app ads.
6. Test Your Idea With an MVP
Testing a telemedicine app with a minimal viable product (MVP) allows entrepreneurs to save a lot of time that they would otherwise spend fixing bugs later on. More importantly, it helps save money. Rather than spending hundreds of dollars on complex functionality at the outset, testing allows you to gather user feedback and focus on the features that have the biggest impact.
7. Research Marketing Channels
To build a successful tele-application, it’s important to plan ahead of the launch how it will be promoted. With that in mind, think about the channels most likely to be used by your targeted audience and allocate a budget for your marketing efforts.

How Much Does It Cost to Build a Telemedicine App?
In keeping with Avenga, the cost of creating a telemedicine app depends on a number of factors, including the feature set, project complexity, UI/UX design, choice of underlying technologies, and developer fees, which can vary greatly.
To give a rough estimate, something simple with just a basic set of features will cost you around $40,000-$50,000, whereas if you decide to build a custom telemedicine app, the price can go up to around $80,000- $200,000.
With this in mind, it’s critical to approach telemedicine app development with care, doing thorough research upfront and validating the business concept with an MVP before deploying a full-scale project.
Conclusion
And this concludes our blog post on “how to build a telemedicine app.”
Telemedicine apps are a great way to access medical services without visiting the clinic in person. There are three main types of telemedicine apps: remote patient monitoring, real-time interactive medicine, and store-and-forward medicine.
This blog also talked about the technologies and the benefits of telemedicine for patients and for doctors.
Each type provides a unique way for patients to access healthcare from the comfort of their own homes. With the continuing advancements in technology, telemedicine apps are becoming increasingly popular and efficient ways of receiving healthcare services quickly and securely.
Author bio:
Dmytro Sokhach is an entrepreneur and the 6-Figure Flipper Club member. Founded Admix Global (web agency) that builds websites, makes them profitable, and sells them as business.